Low-E glass: standard for building thermal insulation
Product Introduction:
BTG anti glare strengthened low e glass
Glass name: factory anti glare strengthened low e low e glass
Other name: supplier anti glare strengthened low e glass, manufacture anti glare toughened low e glass
Glass type: float glass, strengthened glass, low e glass
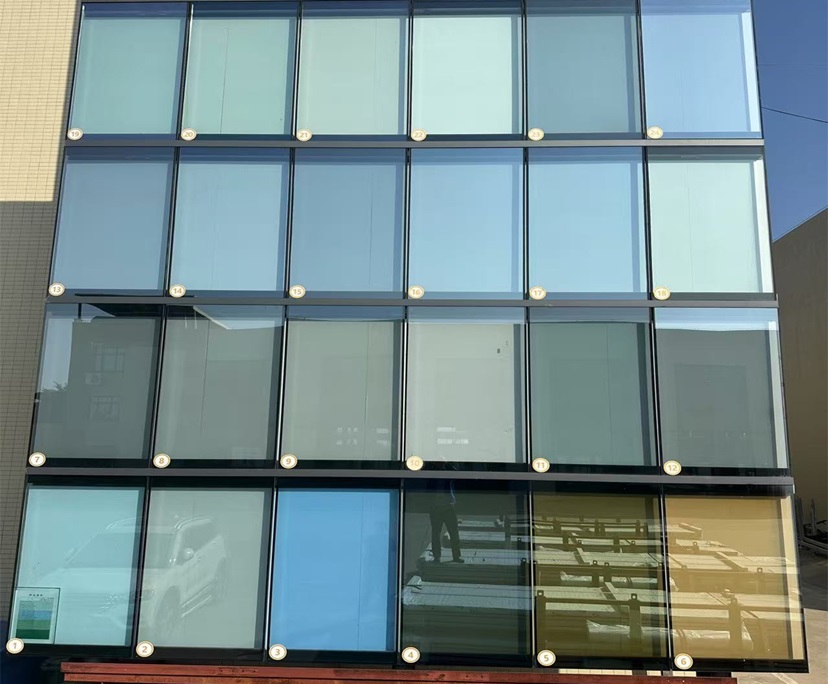
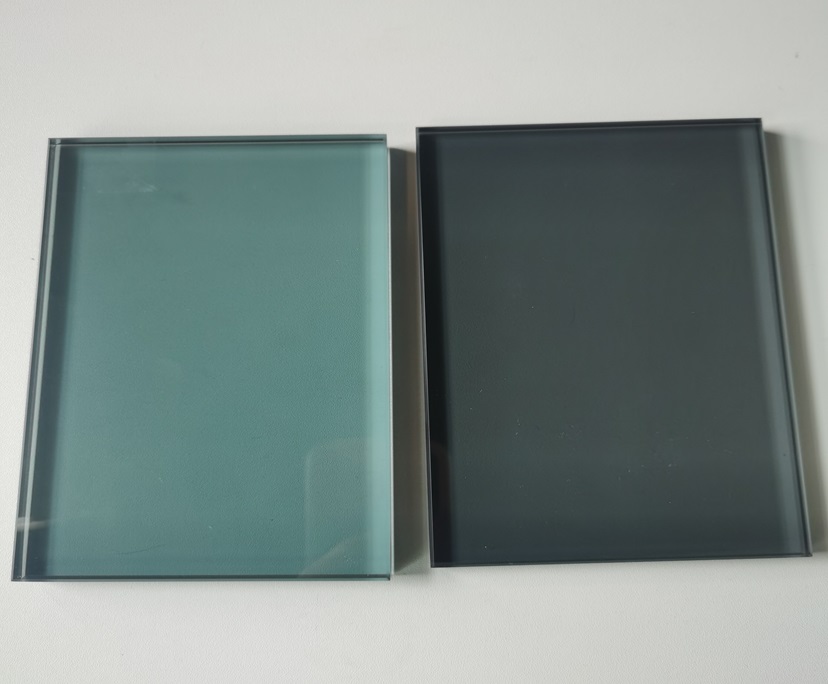
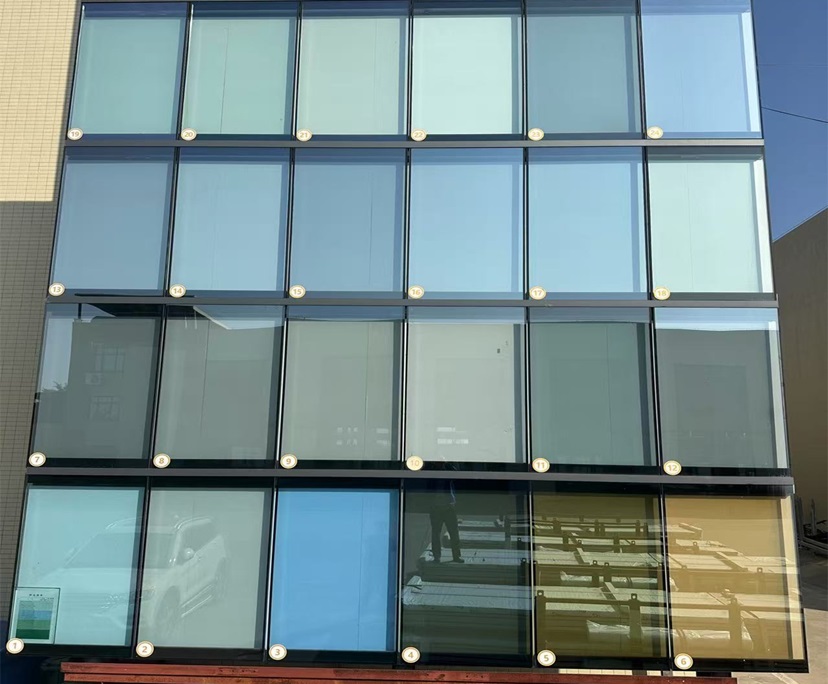
Color: high transparency, grey, green, blue, crystal bronze, black, golden, silver grey, etc.
Certification: BS6206/EN12150/CSI/CE/Intertek
Product details
What is Low-E glass?
Low-E (Low-Emissivity) glass, also known as "low-emissivity glass" in Chinese, is not a new, standalone material. Instead, it's made by depositing one or more nanoscale metal (silver, titanium, etc.) and its oxide thin films onto the surface of high-quality float glass via vacuum
magnetron sputtering or in-line chemical vapor deposition (CVD). This reduces the glass's surface emissivity (E) from 0.84 (of ordinary glass) to below 0.15, potentially as low as 0.01. This allows for high transmittance of visible light and high reflection of mid- and far-infrared radiation.
In short, Low-E glass is an invisible energy-saving filter, allowing light in while trapping heat where it's needed.
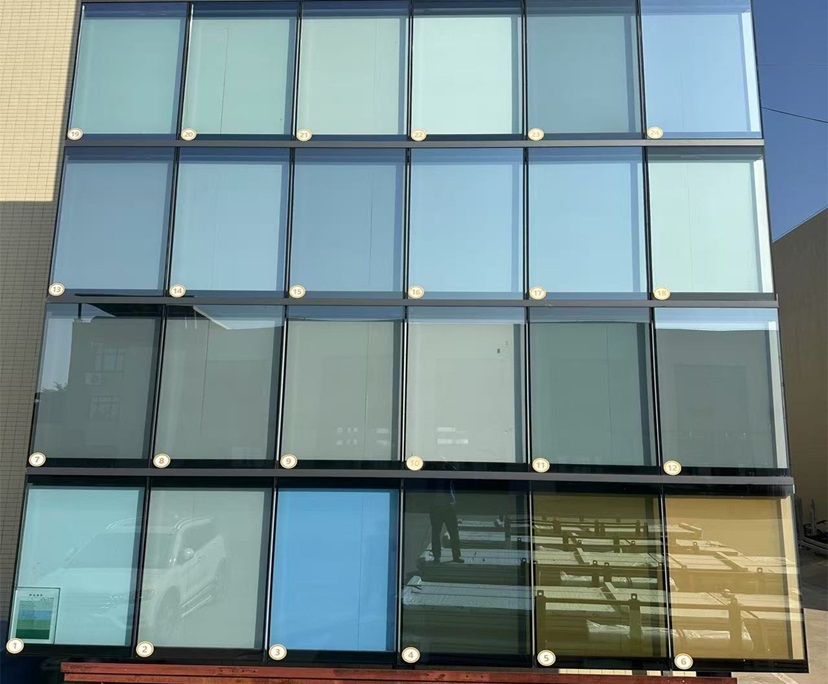

Five Core Features
1. Warm in Winter, Cool in Summer, Year-Round Energy Saving
In winter, far-infrared heat radiation generated by indoor heating is reflected back into the room by the Low-E coating, reducing heat loss. In summer, far-infrared radiation from outdoor sunlight is reflected, reducing air conditioning load. Experiments have shown that Low-E insulating
glass can reduce the K value of building doors and windows to below 1.0 W/(m2·K), reducing cooling and heating energy consumption by an average of 25%–35% year-round.
2. High-definition lighting, say goodbye to "dullness"
Visible light transmittance reaches up to 80%, and the film layer has a neutral color, creating a transparent appearance. Indoor lighting is virtually indistinguishable from natural glass, eliminating the "sunglasses" effect and light pollution associated with traditional coated glass.
3. UV protection, protecting furniture and skin
The silver layer in the film blocks up to 75% of ultraviolet (UV) rays, equivalent to applying SPF 30+ sunscreen to windows. This significantly slows the fading of furniture, flooring, and calligraphy, while also reducing UV damage to human skin.
4. Customizable colors for a beautiful look
Online coating products can achieve a variety of soft tones, including neutral, light gray, silver gray, and blue-green, perfectly matching architectural styles such as modern minimalist, Nordic, and New Chinese, achieving both energy efficiency and aesthetics. 5. Safe Composites for
Enhanced Sound Insulation
Low-E film cannot be used bare on its own; it must be combined into a hollow, laminated, or vacuum structure. When combined with tempered glass, SGP laminated glass, and argon gas filling, the entire glass can simultaneously achieve multiple performance attributes, including
impact resistance, sound insulation (Rw ≥ 35 dB), and a dew point of -60°C without condensation, achieving "one piece, multiple functions."
Application Scenarios
1. Residential Windows and Doors—Living Rooms, South-facing Bedrooms, and Bay Windows
Provides insulation in winter and protection from the west sun in summer, making it particularly suitable for cold winters and hot summers in North, East, and South China. It can also address high wind pressure and noise issues in high-rise residential buildings.
2. Sunrooms, Skylights, and Rooftop Terraces
Large expanses of glass can easily contribute to the "greenhouse effect." Low-E glass reflects the sun's far infrared rays, reducing ceiling temperatures by 8–12°C in summer and eliminating "sauna-like" temperatures. 3. Commercial Curtain Walls and Office Buildings
Reduces peak air conditioning load and reduces curtain wall energy consumption; high-transmittance models ensure natural light indoors, reducing daytime lighting electricity consumption and contributing to LEED, BREEAM, and Three-Star Green Building certifications.
4. Energy-Saving Retrofits for Existing Buildings
No window frames need to be replaced; simply replacing the glass can achieve energy-saving upgrades. The payback period is 3–5 years, and the lifetime electricity cost can be reduced by approximately 150 yuan/㎡ (calculated at 0.9 yuan/kWh in East China).
5. Special Applications
• Hospitals and Libraries: Reduce UV damage to books and medical equipment.
• Museums and Galleries: High-color rendering Low-E glass ensures true-to-life colors for exhibits without yellowing.
• Transportation: Large curtain walls in airports and high-speed rail stations, balancing transparency and energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Low-E glass is more than just a piece of glass; it's a microclimate management system. Its nano-scale coating precisely regulates light and heat, ensuring a constant temperature, quietness, and beauty throughout the seasons. Green energy conservation has become the universal
grammar of global architectural language, and Low-E glass is the most fundamental yet crucial term in this grammar. Choosing Low-E glass means choosing longer-lasting comfort and lower operating costs, while also contributing to global carbon reduction through an invisible force.
Upgrade your window glass now and make your home a "breathing" energy-saving fortress!